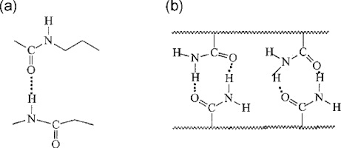
Adhesives are more common in our life, and can not be ignored in life. What kinds of adhesives are there? Let’s take a look.
Polyacrylic resin:
Mainly used in the production of pressure-sensitive adhesives, but also used in textile and construction fields. In recent years, domestic enterprises from abroad introduced several pressure-sensitive adhesive product production lines, promoting the development of domestic polyacrylic resin production technology.
Polyurethane adhesive:
It can bond a variety of materials and maintain the physical and chemical properties of materials at low or ultra-low temperatures after bonding. It is mainly used in shoemaking, packaging, automobiles, magnetic recording materials, and other fields. In recent years, the annual output of polyurethane adhesives in China has increased by 30% on average. About 170 factories in China now produce more than 100 different specifications of such adhesives.
Hot melt adhesive:
Different raw materials can be divided into EVA hot melt adhesive, polyamide hot melt adhesive, polyester hot melt adhesive, polyolefin hot melt adhesive, and so on. At present, the main domestic production and use of EVA hot melt adhesive. The main raw materials of polyolefin series adhesive are ethylene series, SBS, and SIS copolymer.

Epoxy resin adhesive:
Can be used for bonding between metal and most non-metallic materials, and is widely used in construction, automobile, electronics, electrical appliances, and daily household goods. There are more than 100 factories producing epoxy resin adhesives in China, with scattered distribution and an annual output of about 10,000 tons.
Silicone adhesive:
Is a kind of sealing adhesive, with cold resistance, heat resistance, aging resistance, waterproof, moisture-proof, high tensile fatigue strength, small permanent deformation, non-toxic, and so on. In recent years, this kind of adhesive has developed rapidly in China, but at present, the raw material of organic silicon adhesive relies on imports.
Synthetic adhesive:
Mainly used in wood processing, construction, decoration, automobile, shoemaking, packaging, textile, electronics, printing, binding, and other fields. At present, China imports nearly 200,000 tons of synthetic adhesives every year, including hot melt adhesives, silicone sealing adhesives, polyacrylic adhesives, polyurethane adhesives, automotive PVC plastic adhesives, and so on. At the same time, the annual export of synthetic adhesives is about 20,000 tons, mainly polyvinyl acetate, polyvinyl acid formaldehyde, and pressure-sensitive adhesives.
Adhesives for wood processing:
Medium-density fiberboard, gypsum board, plywood, particle board, etc.
Adhesive for construction:
Mainly used for construction decoration, sealing, or bonding between structures. With the development of the construction industry, the development of high-rise buildings, and interior decoration needs, the amount of adhesive used in construction increases sharply. The consumption of building adhesive is about 600 thousand tons above. However, experts think that the product structure of this kind of adhesive needs to be adjusted. At home, building decoration adhesives such as polyvinyl acetate, polyacrylic acid, VAE emulsion, and so on basically can meet the needs, but building sealants and structural adhesives still need to be partly imported from abroad.

Sealing adhesive:
Mainly used for doors, Windows, and prefabricated parts of the house connection. In the past, tung oil mixed with lime was used as a sealant, but now synthetic adhesives must be used for buildings with more than two stories. High-grade sealing adhesive for silicone and polyurethane adhesive, intermediate for neoprene rubber adhesives, polyacrylic acid, and so on. In our country, the construction adhesive market, silicone adhesive, and polyurethane sealing adhesive should be the future development direction, currently, they occupy the sales volume of building sealing adhesive is about 30%.
Adhesive for building structure:
It is mainly used for joining structural units. For example, in the external repair of reinforced concrete structures, metal reinforcement fixing and the construction site construction and epoxy resin series adhesives are generally considered.
Adhesives for cars:
It is divided into 4 kinds, namely, adhesive for the car body, interior decoration, windshield, and chassis of the car body. At present, the annual consumption of automobile adhesives is about 40 thousand tons, among which the biggest use is PVC plastic adhesive, neoprene rubber adhesive, and asphalt series adhesive.

Adhesive for making shoes:
Annual consumption is about 125,000 tons, including 110,000 tons of neoprene adhesive and 15,000 tons of polyurethane adhesive. Because chloroprene rubber adhesives need benzene as a solvent, and benzene is harmful to the human body, development should be limited, so in order to meet the development needs of the footwear industry, polyurethane series adhesives will be the direction.
Adhesive for packaging:
Mainly used to make a pressure-sensitive tape and pressure-sensitive labels, paper, plastic, metal, and other packaging materials surface bonding. The adhesive used for paper packaging material is polyvinyl acetate emulsion. The adhesives used for plastic and metal packaging materials are polyacrylic acid emulsion, VAE emulsion, polyurethane adhesive, and cyanoacrylate adhesive.
Electronic adhesive:
Less consumption, at present less than 10,000 tons per year, most used for integrated circuits and electronic products, is mainly used epoxy resin, unsaturated polyester resin, and silicone adhesive.