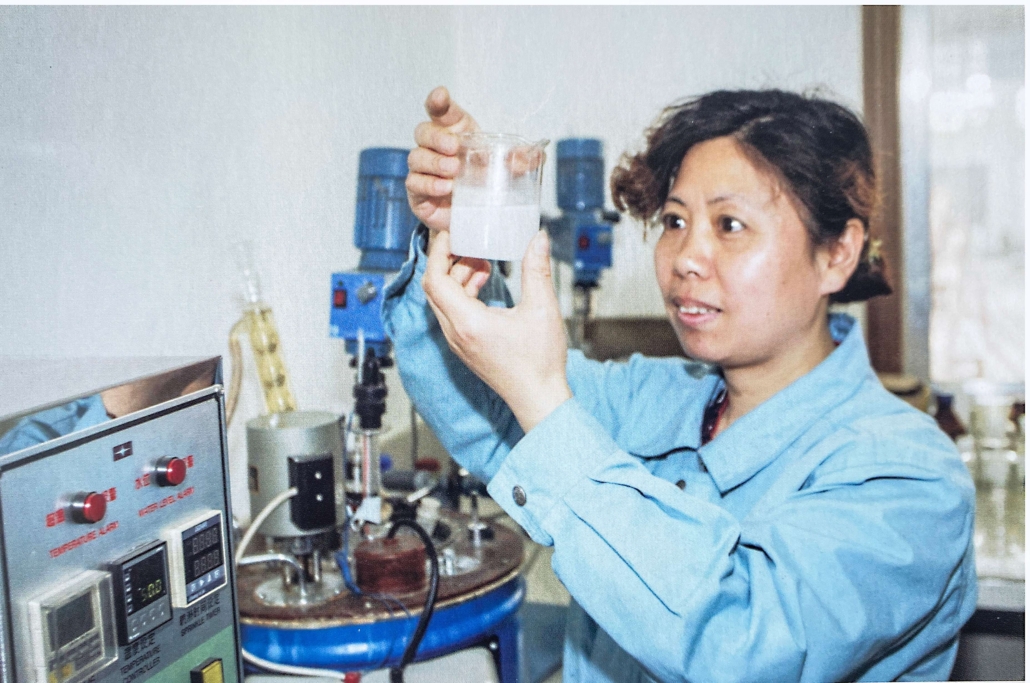
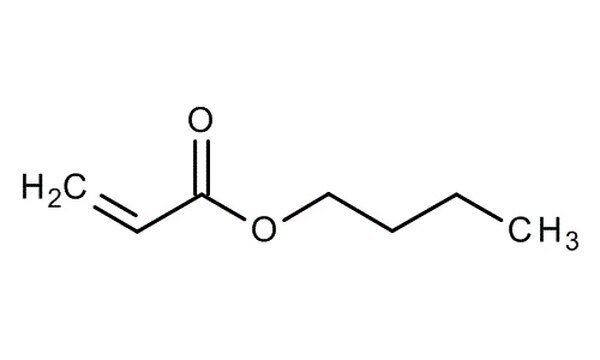
The adhesive film made of polyacrylate latex has a good time, phase aging, shooting oil, and when acid and alkaline performance, and it has good sticky performance for fiber, leather, paper, etc. Therefore, latex is widely used in coatings, fabrics, and tanneries. In the fabric application, it is mainly used as a printing and dyeing adhesive, fabric coating agent, wake-up agent, anti-pilling agent, non-woven products with adhesives, etc.
The development of water-based acrylic copolymer latex has gone through three stages: non-crosslinking, crosslinking, and white crosslinking, but these crosslinking conditions are relatively freezing, requiring higher temperatures (around 160°C) and lower pH values, which wastes resources and increases the damage to the processed substrate and also releases formaldehyde substances that are harmful to humans during the application process.

To implement low-temperature cross-linking of water-based acrylate copolymer latex, some people use an additional catalyst: the use of a mixture of magnesium chloride hexahydrate and citric acid (1:1), such as Azcat A as a catalyst for two-component low-temperature curing adhesives, but the main shortcomings are the use of catalyst, more trouble, and the configuration of the product is not stable, the residual slurry can not be reused. Another way is to adopt radiation-initiated crosslinking technology, but this requires additional special equipment and is costly. There is also a reaction with epichlorohydrin to introduce a reactive epoxy group to replace the formaldehyde-releasing substance N hydroxymethyl acrylamide, but this technology brings the problem of adding AOX pollution to the environment.
The technical problem to be solved is to overcome the above shortcomings and design a special structure of macromolecules and its preparation method so that the main body of the latex formed has a certain degree of pre-crosslinked network structure rather than linear macromolecules.
Therefore, it is necessary to design an environmentally friendly method for the preparation of low-temperature waterborne acrylate copolymer latexes by adding cross-linked components containing two and more diethers to the poly monomers to participate in the copolymerization and introducing a certain degree of cross-linking in the macromolecules during the polymerization process.