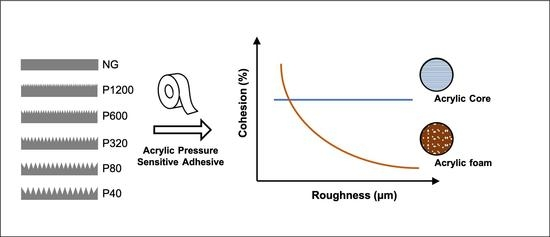
Acrylate pressure sensitive adhesive is the most widely used pressure sensitive adhesive at present
Acrylate pressure sensitive adhesive is the most widely used pressure sensitive adhesive at present, it is the copolymer of an acrylate monomer and another ethylene monomer. Compared with other pressure sensitive adhesives has the following characteristics: almost no need to add antioxidants excellent weather resistance and heat resistance; No phase separation and migration phenomenon, good transparency, and good oil resistance; It has no effect on the skin and is suitable for medical use.
Acrylic emulsion pressure sensitive adhesive has the characteristics of a simple formula, good weather resistance, wide bonding range, and low toxicity, so in recent years, it has been widely used in many fields, from the current practical application of pressure sensitive adhesive comprehensive view, to prepare high strength, good heat resistance pressure sensitive adhesive, simply use one type of resin, difficult to obtain good results, must be modified. Polyacrylate pressure sensitive adhesives are widely used for their excellent bonding properties, chemical stability, non-toxicity, harmless and low cost. However, in order to achieve a better improvement effect, it is very important to select the right functional resin and develop the environment-friendly acrylic emulsion pressure sensitive adhesive with good bonding properties.

In most of the existing solvent polymerization methods for environmental pollution, relatively speaking, emulsion polymerization is a larger trend. Both at home and abroad attach great importance to the emulsion polymerization technology and the development of emulsion adhesive new products, its output increases year by year, the quality is constantly improving, the variety is increasing day by day, and the production process is gradually improving. For acrylate adhesive, the monomer is the base material formed by polymer, different monomer gives different properties of polymer products including hardness, tensile strength, elasticity, adhesion and softness, and other different functions, and determines the physical and mechanical properties of emulsion and latex film.
The glass transition temperature is an important index to reflect the softness and brittleness of the polymer. The higher the glass transition temperature of the homopolymer is called the hard monomer, which can provide the hardness and tensile strength of the copolymer resin. In contrast, the soft monomer refers to the lower glass transition temperature of the homopolymer, which gives the resin certain flexibility and extensibility when participating in resin copolymerization.